2017 - 09 - 11 (월)
기본사항 정리
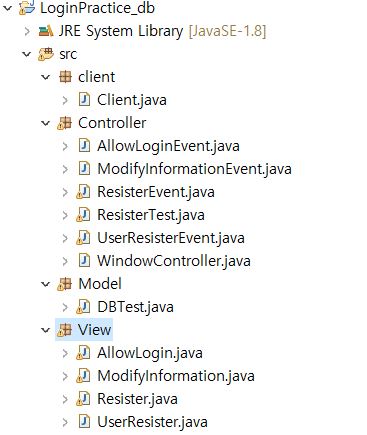
1 . MVC 나누어 보기
아직 MVC구조에 대해서 정확히 아는것은 아니지만 회원가입화면을 만들어 보면서 나누어보았다.
1. 우선 DB SYSTEM계정에 TEST1이라는 테이블 하나를 생성하고 Client패키지에는 고객들의 정보를 담기위해 클래스를 생성해둔다.
2. Model 패키지에는 DBTest라는 클래스를 만들어 DBTest객체를 생성하면 Local DB에 연동되게하였으며 회원가입/탈퇴, 로그인, 회원정보수정 기능을 가진 메소드를 생성하였다.
3. VIEW패키지에는 AWT를 활용하여 화면을 구축하였다.
4. Controller 패키지에는 View 화면에서 어떤 버튼을 클릭하는 이벤트가 발생했을 때 Model에서 정의한 메소드를 호출하여 실행시키는 클래스 및 Main method를 가진 클래스를 생성했다. 또한 WindowEvent를 정의한 클래스를 따로 만들어 각각의 VIEW에서 가져다 쓸 수 있도록 만들었다.
2. Code Source
package client;
public class Client {
private String id;
private String pw;
private String name;
public Client(String id, String pw, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.pw = pw;
this.name = name;
}
//DB에서 정보를 객체로 받아오기위해서 Client 생성자를 만든다.
public Client() {
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getPw() {
return pw;
}
public void setPw(String pw) {
this.pw = pw;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return "id : " +id ;
}
}
//--------------------------------------- Client package DB에서 받을 정보들을 인스턴스 변수로 선언하고 Client 생성자를 만들어 둔다. private로 변수를 정의했기에 getter, setter메소드를 생성.
package View;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.TextField;
import Controller.ResisterEvent;
import Controller.WindowController;
import client.Client;
public class Resister {
ResisterEvent re;
WindowController wc; //WindowController 객체를 생성
public Button bt,bt1;
public Frame frame;
public TextField tfiled,tfiled1;
public Resister(){
frame = new Frame("register");
frame.setSize(1000, 1000);
frame.setVisible(true);
bt = new Button("로그인");
bt1 = new Button("회원가입");
frame.setLayout(null);
Label lid = new Label ("ID:", Label.RIGHT);
Label lid1 = new Label ("PASSWORD:", Label.RIGHT);
tfiled = new TextField(15); // id
tfiled1 = new TextField(15); // pw
frame.add(bt);
bt.setBounds(150, 400, 150, 30);
frame.add(bt1);
bt1.setBounds(350, 400, 150, 30);
frame.add(lid);
lid.setBounds(100, 100, 150, 30);
frame.add(lid1);
lid1.setBounds(100, 150, 150, 30);
frame.add(tfiled);
tfiled.setBounds(250, 100, 150, 30);
frame.add(tfiled1);
tfiled1.setBounds(250, 150, 150, 30);
re = new ResisterEvent(this); //Resisterckass를 매개변수로 하는 ResisterEvent객체 생성
wc=new WindowController(); //WindowController 객체생성
frame.addWindowListener(wc); //본 프레임에 리스너로 WindowController를 적용
bt.addActionListener(re); //버튼 형태의 bt에 ResisterEvent 적용
bt1.addActionListener(re);
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------여기까지가 시작화면 (로그인화면)
package View;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.TextField;
import javax.swing.JPasswordField;
import Controller.UserResisterEvent;
import Controller.WindowController;
public class UserResister {
// 여기가 회원가입화면
public Frame frm;
public Label l1, l2, l3;
public TextField tf1, tf3;
public JPasswordField tf2;
public Button b1, b2;
WindowController wc;
UserResisterEvent ure;
public UserResister() {
frm = new Frame("UserResister");
l1 = new Label("Id를 입력하세요 ", Label.RIGHT);
l2 = new Label("Password를 입력하세요", Label.RIGHT);
l3 = new Label("이름을 입력하세요", Label.RIGHT);
tf1 = new TextField();
tf2 = new JPasswordField();
tf3 = new TextField();
b1 = new Button("등록");
b2 = new Button("취소");
wc = new WindowController();
frm.addWindowListener(wc);
ure = new UserResisterEvent(this);
b1.addActionListener(ure);
b2.addActionListener(ure);
}
/*위에서와 달리 회원가입 화면은 생성자와 메소드로 분류해놓음*/
public void draw() {
frm.setSize(1000, 1000);
frm.setLayout(null);
tf1.setBounds(500, 100, 100, 50);
tf2.setBounds(500, 200, 100, 50);
tf3.setBounds(500, 300, 100, 50);
b1.setBounds(800, 200, 100, 50);
b2.setBounds(800, 300, 100, 50);
l1.setBounds(120, 100, 200, 50);
l2.setBounds(120, 200, 200, 50);
l3.setBounds(120, 300, 200, 50);
frm.add(tf1);
frm.add(tf2);
frm.add(tf3);
frm.add(l1);
frm.add(l2);
frm.add(l3);
frm.add(b1);
frm.add(b2);
frm.setVisible(true);
}
}
//--------------------------------------여기까지가 회원가입 화면
package View;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Label;
import Controller.AllowLoginEvent;
import Controller.WindowController;
import Model.DBTest;
import client.Client;
public class AllowLogin {
public Frame afr;
public Label alb;
public Button abt1;
public Button abt2;
public AllowLoginEvent are;
WindowController wc;
public Client clientInfo;
public AllowLogin(Client client) {
afr = new Frame("AllowLogin");
alb = new Label("로그인 성공");
abt1 = new Button("회원정보수정");
abt2 = new Button("회원탈퇴");
this.clientInfo = client;
}
public void llbDraw() {
afr.setSize(700,700);
afr.setLayout(null);
alb.setBounds(300, 200, 300, 100);
abt1.setBounds(100,500,100,50);
abt2.setBounds(400,500,100,50);
afr.add(alb);
afr.add(abt1);
afr.add(abt2);
afr.setVisible(true);
are = new AllowLoginEvent(this);
wc= new WindowController();
afr.addWindowListener(wc);
abt1.addActionListener(are);
abt2.addActionListener(are);
}
}
//----------------------------------여기까지가 로그인하고난 화면 (회원탈퇴 버튼 생성)
package View;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.TextField;
import Controller.ModifyInformationEvent;
import Controller.WindowController;
import Model.DBTest;
import client.Client;
public class ModifyInformation {
public String id;
public String pw;
public Frame mfr;
public Label mlb,mlb1,mlb2;
public Button mbt,mbt1;
public TextField mtfd1, mtfd2, mtfd;
WindowController wc;
public ModifyInformationEvent mre;
public Resister pre;
public Client clientm;
public ModifyInformation(Client client){
this.clientm = client;
this.id = clientm.getId();
DBTest db = new DBTest();
mfr = new Frame("Modifyer");
mlb = new Label("ID");
mlb1 = new Label("PASSWORD");
mlb2 = new Label("이름");
mbt = new Button("수정 및 저장");
mbt1 = new Button("취소");
mtfd = new TextField();
mtfd1 = new TextField();
mtfd2 = new TextField();
}
// public ModifyInformation() {
// DBTest db = new DBTest();
//
// mfr = new Frame("Modifyer");
// mlb = new Label("ID");
// mlb1 = new Label("PASSWORD");
// mlb2 = new Label("이름");
//
// mbt = new Button("저장");
// mbt1 = new Button("취소");
//
// mtfd = new TextField(db.client.getId().toString());
// mtfd1 = new TextField(db.client.getPw());
// mtfd2 = new TextField(db.client.getName());
// }
public void ModifyDraw(){
mfr.setSize(700,700);
mfr.setLayout(null);
mlb.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 50);
mlb1.setBounds(100,250,300,50);
mlb2.setBounds(100, 400,300, 50);
mtfd.setBounds(400,100,300,50);
mtfd1.setBounds(400, 250, 300, 50);
mtfd2.setBounds(400, 400, 300, 50);
mbt1.setBounds(400,500,100,50);
mbt.setBounds(100,500,100,50);
mfr.add(mlb);
mfr.add(mlb1);
mfr.add(mlb2);
mfr.add(mbt);
mfr.add(mbt1);
mfr.add(mtfd);
mfr.add(mtfd1);
mfr.add(mtfd2);
mre = new ModifyInformationEvent(this);
mfr.setVisible(true);
wc = new WindowController();
mfr.addWindowListener(wc);
System.out.println(clientm.getName());
mbt1.addActionListener(mre);
mbt.addActionListener(mre);
mtfd.setText(clientm.getId());
mtfd1.setText(clientm.getPw());
mtfd2.setText(clientm.getName());
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------여기까지가 회원정보수정화면
package Model;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import client.Client;
public class DBTest {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe";
Connection conn;
PreparedStatement pstmt;
// 받는값 저장
ResultSet rs;
Client client ;
String id = "system";
String pw = "1234";
public DBTest() {
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//url변수에 로컬DB주소를 저장하고 DB연동을위한 Connection 형의 객체를 하나 생성한다.
//SQL문을 날리기위한 PreparedStatement를 생성하고 Select문으로 DB에서 정보를 받아 저장하기 위한 ResultSet 형의 객체하나 생성 이 때 객체로 받아오기위해 Client 형태의 객체하나를 생성한다.
public int add(Client client) {
int i = 0;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, id, pw);
//db에 연결
String sql = "insert into TEST1 values(?,?,?)";
//DB에 날릴 SQL문 ?에는 아래 pstmt객체의 setString으로 넣을 값을 순서대로 세팅한다.
String id = client.getId(); //client객체의 인스턴스 변수가 private로 선언되어있기 떄문에 getID,getPW로 값을 받아서 저장
String pw = client.getPw();
String name = client.getName();
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, id);
pstmt.setString(2, pw);
pstmt.setString(3, name);
i = pstmt.executeUpdate();
//pstmt가 없데이트되면 i값이 올라갈것이다.
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("회원가입 실패");
} finally {
try {
if (pstmt != null)
pstmt.close();
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//pstmt가 비어있을 때 pstmt객체를 닫고 연결이 안되있을 때 conn객체를 닫는다.
}
return i;
}
public Client carry(String id, String pw) {
String loginid = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, this.id, this.pw);
String sql = "select * from TESt1 where id=? and password=?";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, id);
pstmt.setString(2, pw);
//select문으로 받아오기 위해 Resultset형태의 rs객체 하나 생성
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
client = new Client(rs.getString("id"),rs.getString("password"),rs.getString("name"));
}
//rs.next로 테이블형태의 정보를 Client 클래스에서 정의한 매개변수가 있는 생성자를 객체로 생성하여 받아온 정보를 가진 client형태의 객체하나를 생성한다.
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (rs != null)
rs.close();
if (pstmt != null)
pstmt.close();
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return client;
}
public int del(String id) {
int i = 0;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, this.id, this.pw);
String sql = "delete from TEST1 where id=?";
//Delete 문을 보낸다.
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, id);
i = pstmt.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (pstmt != null)
pstmt.close();
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return i;
}
public int modifying(Client modifyClient, String oid) {
//매개변수를 바꿔질 CLIENT의 정보를 가진 modifyClient객체의 참조변수와, String형태의 기존의 client가 가지고있는 id를 매개변수로 지정한다. 이전 아이디 정보가 필요한 이유는 업데이트문에서 where절을 쓰기위함이다.
int i=0;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, this.id, this.pw);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
String sql = "update TEST1 set id= ? , password = ?, name= ? where id = ?";
//update sql문을 보낸다. where절에 들어가는 id=? 는 oid이다.
try {
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
String id = modifyClient.getId();
String pw = modifyClient.getPw();
String name = modifyClient.getName();
pstmt.setString(1, id );
pstmt.setString(2, pw);
pstmt.setString(3, name);
pstmt.setString(4, oid);
i=pstmt.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (pstmt != null)
pstmt.close();
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return i;
}
//다음은 전체보기 메소드인데 만일 ADMIN 페이지를 만들었으면 필요할거 같아서 해보았다.
public ArrayList<Client> allView() {
ArrayList<Client> abc = new <Client>ArrayList();
//ArrayList 형태의 abc객체하나를 생성하고 Client형태로 값을 넣는다.
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, id, pw);
String sql = "select * from TEST1";
//select문으로 TEST1테이블의 모든 ROW를 불러온다.
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
for(int k=0; rs.next(); k++) {
//abc객체에 Client객체 형태로 add한다.(객체배열 생성)
client= new Client(rs.getString("id"),rs.getString("password"),rs.getString("name"));
abc.add(client);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (pstmt != null)
pstmt.close();
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return abc;
}
}
//--------------------------------------여기까지가 Model pacakage의 DBTest 클래스 정의(db연동이 필요한 메소드들 정의)
package Controller;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class WindowController extends WindowAdapter {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
}
//----------------------------Controller package의 WindowController생성하여 windowClosing 이벤트 정의
package Controller;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import Model.DBTest;
import View.Resister;
import View.UserResister;
import client.Client;
public class UserResisterEvent implements ActionListener{
UserResister ure;
DBTest db;
public UserResisterEvent(UserResister ure) {
this.ure =ure;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(e.getSource().equals(ure.b1)) {
String id = ure.tf1.getText();
String pw = ure.tf2.getText();
String name = ure.tf3.getText();
Client client = new Client(id, pw, name);
db = new DBTest();
db.add(client);
System.out.println("등록 성공");
}else if(e.getSource().equals(ure.b2)) {
System.out.println("취소 눌림");
ure.frm.dispose(); // 화면닫힘
Resister re = new Resister();
}
}
}
//----------------------------------------------여기까지가 DBTest의 메소드를 불러와 DB에 INSERT하는 컨트롤러
package Controller;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import Model.DBTest;
import View.AllowLogin;
import View.Resister;
import View.UserResister;
import client.Client;
public class ResisterEvent implements ActionListener {
Resister Re;
public Client clientInfo;
public String id;
public String pw;
public DBTest db;
public ResisterEvent(Resister Re) {
this.Re = Re;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (e.getSource().equals(Re.bt)) {
System.out.println("로그인 눌림");
db = new DBTest();
id = Re.tfiled.getText();
pw = Re.tfiled1.getText();
clientInfo = db.carry(id, pw);
if (!clientInfo.getId().equals(null)) {
System.out.println("로그인 성공");
System.out.println(clientInfo.getId());
Re.frame.dispose();
AllowLogin are = new AllowLogin(clientInfo);
are.llbDraw();
}
} else if (e.getSource().equals(Re.bt1)) {
System.out.println("회원가입 눌림");
Re.frame.dispose(); // 화면닫힘
UserResister ure = new UserResister();
ure.draw();
}
}
}
//--------------------------------------여기까지가 로그인화면에 DBTest 로그인 메소드를 넣는 컨트롤러
package Controller;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import Model.DBTest;
import View.AllowLogin;
import View.ModifyInformation;
public class AllowLoginEvent implements ActionListener{
public AllowLogin are;
public DBTest db;
public AllowLoginEvent(AllowLogin are) {
this.are = are;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(e.getSource().equals(are.abt1)) {
System.out.println("회원정보수정 눌림");
ModifyInformation mre = new ModifyInformation(are.clientInfo);
mre.ModifyDraw();
are.afr.dispose();
//회원 수정창들어갔을 때 회원정보 셋팅
}else if(e.getSource().equals(are.abt2)) {
System.out.println("회원탈퇴 눌림");
db = new DBTest();
if(db.del(are.clientInfo.getId())==1) {
System.out.println("삭제완료");
}
are.afr.dispose(); // 화면닫힘
}
}
}
//-------------------------------여기까지가 로그인 후 화면에 회원탈퇴 기능 넣는 컨트롤러
package Controller;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import Model.DBTest;
import View.ModifyInformation;
import client.Client;
public class ModifyInformationEvent implements ActionListener{
ModifyInformation mre;
DBTest db;
public Client modifyClient;
public ModifyInformationEvent(ModifyInformation mre){
this.mre = mre;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(e.getSource().equals(mre.mbt)) {
//회원정보 수정
System.out.println("회원수정 눌림");
db = new DBTest();
String id = mre.mtfd.getText();
String pw = mre.mtfd1.getText();
String name = mre.mtfd2.getText();
modifyClient = new Client(id, pw, name);
String oid = mre.clientm.getId();
db.modifying(modifyClient, oid);
System.out.println("수정완료");
System.out.println(mre.clientm.getId());
// System.out.println(mre.clientm.getId());
}
else if(e.getSource().equals(mre.mbt1)) {
mre.mfr.dispose();
System.out.println("취소눌림");
}
}
}
//--------------------------------------여기까지가 회원수정 메소드를 불러와 실행시키도록 하는 컨트롤러
package Controller;
import Model.DBTest;
import View.Resister;
public class ResisterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Resister re = new Resister();
// DBTest db = new DBTest();
// System.out.println(db.allView().get(0).getId());
// System.out.println(db.allView().toString());
}
}
//-------------------------여기까지가 main문