2018 - 02 - 22 (목)
백준알고리즘 재귀 & 메모이제이션
- 재귀함수
재귀 함수로 Factorial 함수 만들기 : 재귀를 사용할 경우 가독성이 뛰어나고 코드를 축소할 수 있어서 좋으나 성능상으로는 컴퓨터에 부담을 주기에 좋은 방법은 아니다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Memoization {
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(factorial(2));
System.out.println(factorial(3));
//재귀 함수를 활용한 factorial
}
static int factorial(int number){
if(number>0){
return number*factorial(number-1);
}else{
return 1;
}
}
}
- 메모이제이션
위에서 작성한 재귀함수로 Factorial 함수를 구현할 경우 factorial(2) 를 연산 하고 factorial(3)을 연산한다. 이 떄 factorial(3)의 경우 factorial(2) * 3을 하면 계산이 가능하다. 즉 중복된 연산이 있을 경우 메모이제이션을 활용하면 효율적이다. facotiral(2) 를 메모리에 남겨두어 재사용하는 것이다.
메모이제이션의 경우 반복할 횟수가 높을 수록 그 진가를 발휘한다.
메모이제이션으로 factorial 만들기
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Memoization {
public static void main(String args[]){
long before, after = 0;
before = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(factorial(30));
System.out.println(factorial(30));
after = System.currentTimeMillis();
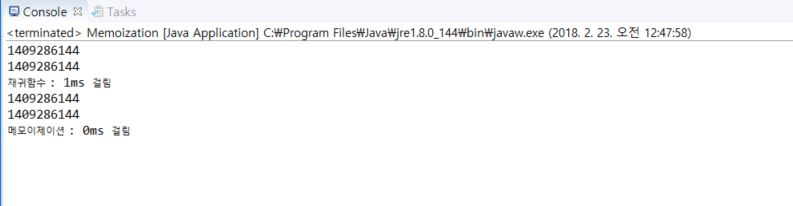
System.out.println("재귀함수 : "+ (after-before) + "ms 걸림");
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
before = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(factorialMemoization(30, map));
System.out.println(factorialMemoization(30, map));
after = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("메모이제이션 : "+ (after-before) + "ms 걸림");
//재귀 함수를 활용한 factorial 함수
}
static int factorial(int number){
if(number>0){
return number*factorial(number-1);
}else{
return 1;
}
}
// 메모이제이션을 적용한 factorial 함수
static int factorialMemoization(int number, HashMap map){
if(map.containsKey(number)){
return (int) map.get(number);
}else{
if(number>0){
int temp = number*factorial(number-1);
map.put(number, temp);
return temp;
}else{
return 1;
}
}
}
}
위 처럼 재귀함수보다 더 빠른 성능을 보여준다.